How to Ping an Ip Address One Second Stop a Minutes and Ping Again
Pinging an IP accost
This article explains how to ping an IP address for a device. The goal of pinging a device is to discover out if a device is reachable at a particular IP accost.
Ping is a computer network administration utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the circular-trip time for letters sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
A device on a computer network should respond to a repeat asking (ping) with an echo respond (pong) confirming it is online. This respond should come within milliseconds. If a answer does not come it is said to have "timed out" because the predefined wait time for a answer has been exceeded. If no reply is seen nosotros typically assume that no device is present at, or assigned with, that IP accost.
Getting connected
For the purposes of this article we will use a computer running Windows seven. Other Microsoft operating systems since Windows XP volition employ approximately the same procedure.
Connection is made via an Ethernet cablevision either straight between your computer's NIC and the Biamp device via a crossover cable, or via a network switch to a Biamp device on a network. Either connection type will let you lot to Ping the device's presumed address and see if a device responds from that location.
cmd.exe
Brainstorm by going to the Windows start bill of fare.
Type the letters "cmd" into the Search box and striking Enter.
This will ask the Windows OS to run cmd.exe, commonly referred to as the "Command Prompt" interface. The post-obit window should open up on your desktop.
Ping
The Control Prompt allows diverse commands and queries to be sent to the organisation. For a Biamp device with the default IP address you volition employ the command " ping 192.168.1.101 ". If the device is at a unlike IP address, replace 192.168.ane.101 with the address you are trying to poll.
Afterward you lot hit Enter the request will be sent 4 times, generating either a time out failure or a reply with round trip statistics.
To try again, hit the Upwards arrow key in one case to refresh the final control, and then Enter.
Failures can present in a few means, here is what yous might expect to see dorsum:
Two Ping failures are shown with slightly different feedback but no response from the intended device.
Bank check the cabling, ensure the concrete path to the device is sound, and try again.
Success!
4 responses with good, quick response times.
Continuous ping
Employ the command " ping 192.168.1.101 -t " to initiate a continuous ping. Once again, replace the IP address with one specific to your device equally needed. The -t tin be placed before or later the IP address.
Interrupt the pings with Ctrl-Suspension to see statistics on the captures.
Terminate the pings with Ctrl-C.
" ping –t 192.168.1.101 >PingLog.txt " will output the ping results to a txt file called "PingLog.txt", it volition not bear witness a scrolling trace in the cmd prompt window. It will exist placed in the C:\Users\username directory. Change the file name so each is unique. Pings volition happen in one case a second. control-C will end the ping and close the file.
Things you can ping
Ping is not express to nearby hardware, you lot tin can also ping websites.
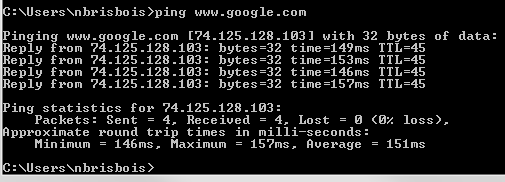
A ping to google.com
Or ping your ain NIC.
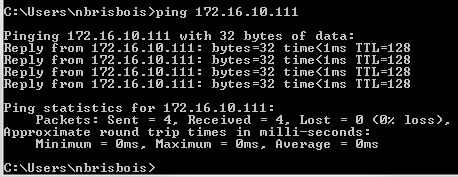
Note that the maximum round trip time for your own NIC is typically well-nigh 0ms.
Ping a range of IP addresses
In some situations you need to ping a device but don't know where it lies within the subnet range. This method can assistance narrow down the list of addresses being used.
In Windows, open the command prompt (Windows showtime menu > Search > type "cmd")
Fast ping time
From the command prompt, type....
for /50 %i in (1,i,254) do @ping 192.168.1.%i -westward 10 -n 1 | discover "Reply"
This will ping all addresses from 192.168.1.i to 192.168.1.254 1 time each, await 10ms for a reply (more than enough time on a local network) and prove merely the addresses that replied.
Variables:
- Alter the IP address after @ping to reflect your network's IP range.
- Syntax for for /l is (get-go,step,end) if y'all want to change the range to scan.
- The -west 10 tells it to only wait 10 ms for a reply before moving on. If your network is slow you lot will accept to increase this value or have information technology out all together, although this will brand it very slow.
- The vertical line character earlier find is typed as shift-\ on the Windows keyboard.
Also, note that the Windows find is case sensitive, so make certain you capitalize "Answer" or you lot won't get any output. Optionally you tin merely blazon "eply" and it will automatically add the uppercase R in the response.
Longer ping fourth dimension
This is the same equally higher up, with the -westward variable changed to let a 100ms reply window.
for /l %i in (one,1,254) practice @ping 192.168.1.%i -w 100 -n 1 | detect "Reply"
This will ping all addresses from 192.168.ane.1 to 192.168.1.254 one time each, wait 100ms for a respond and prove just the addresses that replied.
Ping from a specific NIC
To specify the source interface to utilize, use the -s option. (Yous use the interface number, not the IP address). To place the NIC interface number use the control " netsh int ipv4 show interfaces "
To forcefulness IPv4 or IPv6, apply -4 or -6.
To ping 192.168.0.1 using ipv4 from interface 1, use the command " ping -4 192.168.0.1 -south 1 "
Ping to exam MTU size
A standard ping packet is 32 bytes. The ping command supports a length (-l, lowercase L) attribute which allows you to define the ping bundle size. This allows you to test the maximum packet size you can transport between 2 devices. The -f aspect sets a Don't Fragment (DF) flag in the packet (IPv4-only) which keeps the package size intact.
Multiple pocket-sized TCP packets may be aggregated by a switch to optimize manual speed and latency. If the aggregating switch builds a packet of 1500 bytes and the transmission path has another switch which only allows a maximum of 1492 bytes the bundle will be lost en route, as it volition non be able to pass the restriction. The lowest MTU (maximum transmission unit) seen on a path will be the brake. All switches on a path should permit the aforementioned MTU size.
A ping bundle contains some overhead data, 20 bytes are reserved for the IP header and 8 bytes are allocated to the ICMP Repeat Request header. Add these 28 bytes to the length value yous specify to become the full packet size. E.thousand. For a full parcel size of 1500 bytes you would subtract 28 bytes from 1500 for a length of 1472
" ping 192.168.0.1 -f -l 1472 "
Success looks like a standard ping response, failure yields the message " Packet needs to exist fragmented but DF set."
C:\WINDOWS\System32>ping 192.168.0.i -f -l 1472
Pinging 192.168.0.ane with 1472 bytes of information:
Reply from 192.168.0.one: bytes=1472 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=1472 time=1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=1472 time=5ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=1472 time=1ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.1:
Packets: Sent = four, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 5ms, Boilerplate = 1ms
C:\WINDOWS\System32>ping 192.168.0.1 -f -l 1550
Pinging 192.168.0.1 with 1550 bytes of data:
Packet needs to exist fragmented only DF set.
Parcel needs to be fragmented but DF set.
Bundle needs to be fragmented but DF fix.
Parcel needs to exist fragmented but DF set.
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.1:
Packets: Sent = iv, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
Pathping
The pathping command is a combination of ping and tracert using ICMP messages. It tin can be a helpful tool for testing a routed path betwixt devices.
" pathping 192.168.0.i "
ARP
To observe the MAC accost of the device at a specific address you lot can send the arp -a control followed by the IP address of the device.
Alternately, yous can arp for all devices on the network using just the arp -a command.
PowerShell
Open PowerShell (in the Windows menu search bar type 'Powershell') and copy / paste these commands with the appropriate IP accost for the device under test.
If lines paste in reverse order using right-click information technology may be necessary to enable paste using CTRL+5 in the PowerShell properties Options tab.
Continuous Ping
You lot can apply Wndows PowerShell to create a continuous ping examination.
Ping.exe -t 192.168.one.101
You can utilise Wndows PowerShell to create a logged continuous ping exam.
Ping.exe -t 192.168.ane.101 | ForEach-Object {"{0} - {ane}" -f (Get-Date),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\ping-192-168-1-101.log -Append
The continuous ping will run until the PowerShell window is airtight. The log output will look like this (intermediate log data has been cut out)
12/22/2021 3:51:31 PM - Pinging 172.30.41.56 with 32 bytes of data:
12/22/2021 3:51:31 PM - Reply from 172.30.41.56: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
12/22/2021 iii:51:32 PM - Reply from 172.xxx.41.56: bytes=32 fourth dimension<1ms TTL=64
12/22/2021 3:51:33 PM - Reply from 172.30.41.56: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
...
12/28/2021 11:05:04 AM - Reply from 172.xxx.41.56: bytes=32 fourth dimension=1ms TTL=64
12/28/2021 11:05:05 AM - Reply from 172.30.41.56: bytes=32 fourth dimension=1ms TTL=64
12/28/2021 11:05:06 AM - Reply from 172.30.41.56: bytes=32 fourth dimension=1ms TTL=64
12/28/2021 11:05:07 AM - Answer from 172.30.41.56: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
12/28/2021 eleven:05:07 AM -
12/28/2021 eleven:05:07 AM - Ping statistics for 172.30.41.56:
12/28/2021 11:05:07 AM - Packets: Sent = 498410, Received = 498410, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
12/28/2021 11:05:07 AM - Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
12/28/2021 11:05:07 AM - Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 124ms, Boilerplate = 0ms
Open TCP port examination
You can do a simple one time test of a port using the following command, exist certain to enable HTTPS in Tesira Device Maintenance'southward Network Settings if a "true" consequence is desired::
Test-NetConnection -Port 443 -ComputerName 192.168.1.101 -InformationLevel Detailed | Format-List *
You lot tin can run an extended exam of an open port using this command set. This example runs for 720 minutes (12 hours) testing the port using TCP once a infinitesimal and logging success (true) or failure (false) with the engagement and fourth dimension.
$timer = new-timespan -Minutes 720
$clock = [diagnostics.stopwatch]::StartNew()
while ($clock.elapsed -lt $timer){
$command=Examination-NetConnection -Port 443 -ComputerName 192.168.1.101 -InformationLevel Quiet | ForEach-Object {"{0} - {1}" -f (Become-Date),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\check-192-168-1-101-port-443.log -Append
cls
$command
start-sleep -seconds lx
}
write-host "Timer end"
The continuous port test will run until the timer expires or the PowerShell window is airtight. The log output will look like this (intermediate log data has been cut out)
12/28/2021 nine:00:xv AM - Truthful
12/28/2021 9:01:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 nine:02:15 AM - Truthful
12/28/2021 nine:03:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 9:04:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 9:05:xv AM - True
12/28/2021 ix:06:xv AM - True
12/28/2021 nine:07:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 ix:08:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 9:09:15 AM - True
12/28/2021 9:10:16 AM - True
A test for multiple open TCP ports on 1 or more than devices tin can be run using the script below.
# Biamp Tesira port test
#
# Outputs a unique log file for each IP accost saved in C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log
# To relieve i file per port per device edit the two appearances of C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log to C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr-$Port.log
# Output reports results evidence in real-time in Powershell window
# If a device/port fails to respond it will delay the next test as Test-NetConnection retries the device
#
$Ports = 22,23,80,443,61451 #TCP ports to test
# 22 SSH, 23 Telnet, lxxx HTTP (open if HTTPS is activated), 443 HTTPS, 61451 Tesira discovery and communication
# for models that do not support HTTP/HTTPS ports 80 and 443 can be omitted
#
$Ipaddrs = '172.30.41.50', '172.xxx.41.53', '172.30.41.54' # IP addresses to test
#
$timer = new-timespan -Minutes 10 # examination duration
# Duration of test in minutes 240 = four hrs, 480 = 8 hrs, 720 = 12 hrs, 960 = 16hrs, 1200 = 20 hrs, 1440 = 24 hrs, 2880 = 48 hrs, 4320 = 72 hrs
#
$clock = [diagnostics.stopwatch]::StartNew()
Foreach ($Ipaddr in $Ipaddrs){ # open welcome message
"Begin $timer test period for $Ipaddr ports $ports"| ForEach-Object {"{0} - {ane}" -f (Get-Engagement),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log -Append
} # close welcome message
while ($clock.elapsed -lt $timer)
{ # open test period
$elapsed = $clock.elapsed
$sofar = $elapsed.ToString("hh' hrs 'mm' min 'ss' sec'")
$i++
#
Foreach ($Ipaddr in $Ipaddrs){
"Test period elapsed time $sofar for $IPAddr. Test cycle $i" | ForEach-Object {"{0} - {1}" -f (Get-Date),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log -Suspend # notes how long examination has run so far
Foreach ($Port in $Ports){
$portelapsed = $clock.elapsed
$portsofar = $portelapsed.ToString("hh'h'mm'm'ss\.ff'southward'")
if
(Exam-NetConnection -ComputerName $Ipaddr -Port $Port -InformationLevel Quiet -WarningAction SilentlyContinue)
{"Pass $Ipaddr Port $Port is OPEN at elapsed time $portsofar"| ForEach-Object {"{0} - {i}" -f (Get-Appointment),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log -Append}
else
{"---- $Ipaddr Port $Port is UNREACHABLE at elapsed time $portsofar" | ForEach-Object {"{0} - {1}" -f (Get-Engagement),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log -Append}
}
}
start-sleep -seconds 60 #Time to await between port scan tests
} # close test period
Foreach ($Ipaddr in $Ipaddrs){ # open up completed test message
"Examination period duration $timer is complete for $Ipaddr after $i tests"| ForEach-Object {"{0} - {ane}" -f (Get-Date),$_} | Tee-Object C:\Temp\PortTest-$Ipaddr.log -Append
} # shut completed examination message
$i = 0 # reset count
write-host "All tests completed." # completed test message, for last only
Trace route
Trace road or trace road with hop latency. The -Hops variable limits how many hops are shown.
Test-NetConnection 172.30.41.50 -traceRoute
or
Test-NetConnection 172.30.41.50 -traceRoute -Hops 10 | select-object TraceRoute | foreach-object {test-connection $_.TraceRoute -count 1}
Source: https://support.biamp.com/General/Networking/Pinging_an_IP_address
0 Response to "How to Ping an Ip Address One Second Stop a Minutes and Ping Again"
Post a Comment